
Sea Ice Today
Analyses and daily images of sea ice conditions
Analyses
Filter by:

Beginning October 15, 2025, NSIDC’s Sea Ice Today services will be reduced because of non-renewed funding.
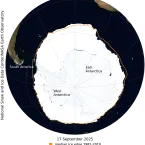
Antarctica
Southern Hemisphere
On September 17, Antarctic sea ice likely reached its annual maximum extent of 17.81 million square kilometers (6.88 million square miles). The 2025 maximum is the third lowest in the 47-year satellite record above 2023 and 2024.

Northern Hemisphere
Arctic
On September 10, Arctic sea ice likely reached its annual minimum extent of 4.60 million square kilometers (1.78 million square miles). The 2025 minimum shares the tenth lowest spot in the nearly 47-year satellite record with 2008 and 2010.

Northern Hemisphere
Arctic
In August, sea ice rapidly melted and compacted north of Alaska in the Beaufort Sea, initiated by a warm pulse of air from east Siberia that was sustained by persistent winds from the southwest. However, the overall pace of decline for the month was near average. Antarctic sea ice climbed in August but remained well below average, ending at third lowest extent.

Antarctica
Arctic
At the end of July 2025, daily sea ice extent in both hemispheres ranked third lowest in the 47-year satellite record. For most of the month, Arctic sea ice extent tracked close to levels recorded for 2012, the record-low-September year.

Antarctica
Arctic
Arctic sea ice extent tracked at near-record low levels through much of June, hitting daily record low levels from June 20 to 26. Antarctic sea ice averaged third lowest for the month of June. There have been unrecoverable gaps in delivered sea ice data from the Defense Meteorological Satellite Program (DMSP) Special Sensor Microwave Imager/Sounder (SSMI/S). Since the the SSMIS data feed will end July 31, the team will be switching to the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) Advanced Microwave Scanning Radiometer-2 (AMSR2) passive microwave sensor as the primary data source.

Antarctica
Northern Hemisphere
Arctic
May sea ice extent in the Arctic averaged 12.56 million square kilometers (4.85 million square miles), tying with 2004 for seventh lowest on the 47-year satellite record. Antarctic sea ice extent for May was fifth lowest in the satellite record, but below average growth through the month resulted in the daily ice extent moving away from the 1981 to 2010 average.

Antarctica
Arctic
Arctic sea ice extent through most of April changed very little. Only at the end of the month did extent begin to decline. Because the month started with unusually low extent, however, the average extent for April ended up tied for ninth lowest in the satellite record. The situation in the Antarctic remained fickle. Extent at the end of the month was tracking near the levels recorded for 2024, but well above the record low in 2023.

Antarctica
Arctic
Arctic sea ice extent for March set a record low in the 47-year satellite data record. Extent was below average everywhere except the East Greenland Sea.

Northern Hemisphere
Arctic
Arctic sea ice extent appears to have reached its annual maximum on March 22, 2025. This is the lowest maximum in the 47-year satellite record, with previous low maximums occurring in 2017, 2018, 2016, and 2015.

Antarctica
Southern Hemisphere
On March 1, Antarctic sea ice likely reached its minimum extent of 1.98 million square kilometers (764,000 square miles), tying for second lowest extent with 2022 and 2024 in the 47-year satellite record. This is the fourth consecutive year that Antarctic sea ice has reached a minimum below 2.0 million square kilometers (772,000 square miles).

Antarctica
Arctic
Arctic sea ice growth was slow in February, leaving extent at record-low levels for the end of the month. In the Antarctic, the annual minimum in extent is imminent, and near a record low.

Antarctica
Arctic
Arctic daily sea ice extent continued to hover near record daily lows in January, with the ice edge well northward of its long-term average position in most areas. In contrast to the cold conditions dominating the contiguous United States, much of the Arctic experienced above-average January temperatures. In the Antarctic, daily sea ice extent fell below the long-term average after a brief period of above-average daily extents, ending the month just above the lowest 25 percent of ice extents for the day.

Antarctica
Arctic
Air temperatures in December 2024 were above average over the entire Arctic Ocean, continuing the pattern set in November. Average Arctic sea ice extent for December was the lowest in the satellite record, in considerable part due to delayed ice growth in Hudson Bay and low extent in the northern Barents Sea. Antarctic sea ice has declined at a slower-than-normal pace since mid-November, erasing the record and near-record low extents of October and November and finishing the year very close to the 1981 to 2010 average.

Antarctica
Arctic
Following the pattern seen in recent years, autumn freeze up has been slow in the Arctic, reflecting the growing heat gain in the ocean mixed layer during summer and higher air temperatures. In the Antarctic, the rate of spring ice loss slowed somewhat during November, ending the month above the extreme low levels of 2016 and 2023.

Antarctica
Arctic
As darkness extends southward across the Arctic, sea ice has advanced to much of the Russian shoreline, but growth has been particularly slow in the Barents and Kara Seas. In the Antarctic, with the onset of spring, the pace of seasonal sea ice loss has increased.

Antarctica
On September 19, Antarctic sea ice likely reached its annual maximum extent of 17.16 million square kilometers (6.63 million square miles). The 2024 maximum is the second lowest in the 46-year satellite record above only 2023.

Antarctica
Northern Hemisphere
Southern Hemisphere
Arctic
Since 2007, the Arctic sea ice minimum has dropped below 5 million square kilometers (1.93 million square miles) every year, except in 2009, 2013, and 2014, when extent barely crossed the 5 million square kilometer mark. Such low extents would have been hard to imagine in the 1990s, when extent averaged 6.46 million square kilometers (2.49 million square miles). Arctic climate warming continues to lead an unfortunate path of change for the planet. Here, NSIDC researchers summarize this year’s events in the Arctic, and touch upon Antarctica sea ice extent at the end of its austral winter.

Northern Hemisphere
Arctic
On September 11, Arctic sea ice likely reached its annual minimum extent of 4.28 million square kilometers (1.65 million square miles). The 2024 minimum is the seventh lowest in the nearly 46-year satellite record. The last 18 years, from 2007 to 2024, are the lowest 18 sea ice extents in the satellite record.

Antarctica
Arctic
With the waning of sunlight, the pace of sea ice loss in the Arctic is slowing, and the seasonal minimum is expected in mid-September. While a new record low is highly unlikely, extent at the beginning of September is below many recent years. Antarctic ice extent is approaching its seasonal maximum and is near last year's record low.