GLIMS: Global Land Ice Measurements from Space
Overview
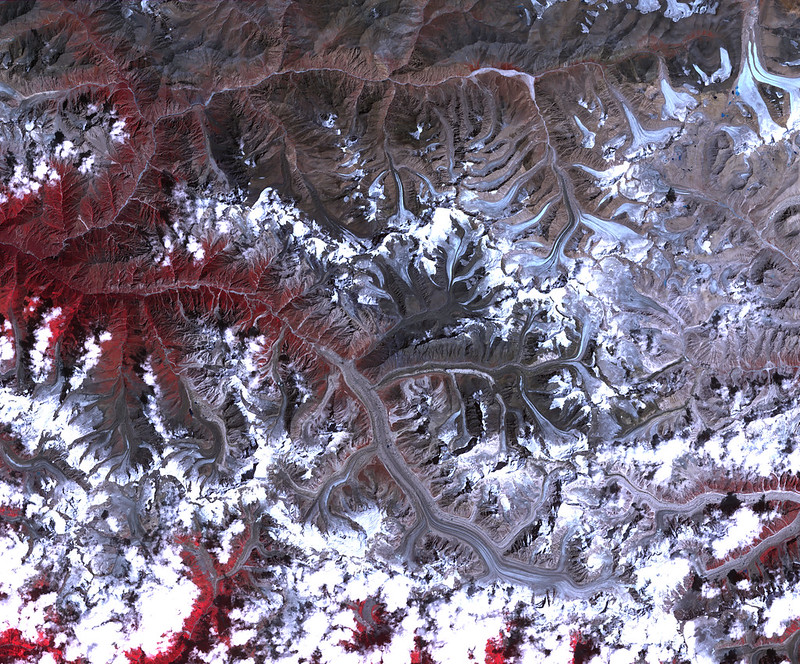
The NSIDC DAAC GLIMS data collection includes data from the Global Land Ice Measurements from Space (GLIMS) initiative. GLIMS is an international project to inventory the world’s glaciers and to create a comprehensive, global database of land ice through repeat surveys.
This data collection’s primary data product is the GLIMS Glacier Database. The glacier database includes measurements of glacier geometry, glacier area, snowlines, supraglacial lakes and rock debris, and other glacial attributes, as well as browse images. The collection includes data from approximately 70 percent of the world's 200,000 glaciers, and new glaciers are continually added. Data are primarily derived from the Advanced Spaceborne Thermal Emission and Reflection Radiometer (ASTER) instrument aboard the Terra satellite and the Landsat Enhanced Thematic Mapper Plus (ETM+), but other sources are also used. These additional sources include other satellite observations, such as observations from Satellite Pour l’Observation de la Terre (SPOT) and EMI+, as well as maps, aerial photographs, and historical observations dating back to 1850.
The GLIMS initiative was established in 1999 by the joint U.S./Japan ASTER Science Team. It is a collection of worldwide cooperative networks (Regional Centers) that map and analyze glacier fluctuations in their geographic region of expertise. Since its inception, over 60 institutions in 28 nations worldwide have contributed to the GLIMS Glacier Database.
Because glaciers advance and retreat in response to environmental cues, including changes in temperature and precipitation, they are strong indicators of climate change. The GLIMS Glacier Database enables scientists to map how glaciers have changed over time, allowing them to better understand the impacts these changes will have on water resources, downstream hazards, ecosystem changes, and global sea level rise.
The Randolph Glacier Inventory (RGI), which is a global catalog of glacier outlines, is derived from and supplements the GLIMS Glacier Database. While GLIMS is multi-temporal (meaning that it has outlines for multiple years for any particular glacier), the RGI includes a single outline of the extent of each glacier, chosen to be close to the year 2000. The RGI is distributed in shapefile format, while GLIMS data can be downloaded in a few formats, packaged on-demand.
NSIDC also provides information on more than 130,000 glaciers through the World Glacier Inventory.
Parameters
Glacier area, geometry, surface velocity, and snow line elevation
Spatial coverage
Global
Related collection(s)
Explore images from GLIMS