
Sea Ice Today
Analyses

Arctic sea ice extent for November 2019 ended up at second lowest in the 41-year satellite record. Regionally, extent remains well below average in the Chukchi Sea, Hudson Bay, and Davis Strait.
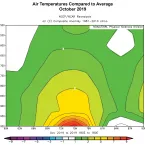
October daily sea ice extent went from third lowest in the satellite record at the beginning of the month to lowest on record starting on October 13 through October 30.

Arctic sea ice began its autumn regrowth in the last 12 days of September, with the ice edge expanding along a broad front in the western Arctic Ocean.
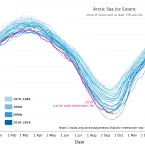
On September 18, Arctic sea ice reached its likely minimum extent for 2019.

The end of the Arctic sea ice melt season is nigh. The last couple of weeks have seen small rises and falls in ice extent, primarily due to changes in wind patterns.
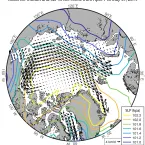
While Arctic sea ice extent was tracking at record low levels in July and August, the pace of ice loss slowed considerably after the middle of August, despite above-average air temperatures over much of the Arctic Ocean.
Arctic sea ice extent in July tracked at record low levels for multiple individual days and for the month as a whole.
Loss of ice extent through the first half of July matched loss rates observed in 2012, the year which had the lowest September sea ice extent in the satellite record.
After a period of slow ice loss in the middle of June, Arctic sea ice loss ramped up, and extent at the end of the month fell below 2012, the year which ended up with the lowest September ice extent in the satellite record.
May saw above average temperatures over nearly all of the Arctic Ocean, Baffin Bay, and Greenland. Early sea ice retreat in the Bering Sea extended into the southern Chukchi Sea. Northern Baffin Bay and the Nares Strait have low ice cover.
April reached a new record Arctic low sea ice extent. Sea ice loss was rapid in the beginning of the month because of declines in the Sea of Okhotsk.
Arctic sea ice extent appears to have reached its maximum extent on March 13, marking the beginning of the sea ice melt season. Since the maximum, sea ice extent has been tracking at record low levels.
Arctic sea ice appears to have reached its annual maximum extent on March 13, tying with 2007 for seventh lowest in the 40-year satellite record. The 2019 maximum sea ice extent is the highest since 2014.
Arctic sea ice extent for February 2019 was the seventh lowest in the satellite record for the month, tying with 2015. So far this winter, sea ice extent has remained above the 2017 record low maximum.
In January 2019, a pattern of high-altitude winds in the Arctic, better known as the polar vortex, weakened, sweeping frigid air over North America and Europe in the second half of the month.
As 2018 came to a close, Arctic sea ice extent was tracking at its third lowest level in the satellite record, while sea ice in the Antarctic remained at historic lows.
As of January 1, 2019, Antarctic sea ice extent had experienced several days of record lows.
The Arctic freeze-up season is well underway, with ice extent increasing faster than average for most regions in November. Exceptions were in the Chukchi and Barents Seas, where the ice has been slow to form.
Over the Pacific side of the Arctic, a pattern of unusual warmth noted in last month’s post continued.
