
Sea Ice Today
Analyses
Arctic sea ice extent continues its seasonal decline. Through most of June the pace of decline was near average, but increased towards the end of the month.
Arctic sea ice extent declined at a typical rate through May, but extent remained below average for the period of satellite observations.
Since reaching its annual maximum extent on March 21, Arctic sea ice extent has declined somewhat unevenly, but has consistently been well below its average 1981 to 2010 extent.
While the eastern half of the United States has dealt with a cold and snowy winter, temperatures in the Arctic have been distinctly higher than average. The warm conditions have led to a slower than average expansion of the winter ice cover.
Arctic sea ice extent remained lower than average in January, and just within two standard deviations of the long-term average. Arctic temperatures remained above average, even as cold winter air embraced North America.
Daily sea ice growth rates were variable during December. By the end of the month, ice extent remained below average in most of the far north.
Ice extent in the Arctic was below average during November. There was substantially less ice than average in the northern Barents Sea, likely due to an influx of warm ocean waters and the persistence of a strong positive Arctic Oscillation (AO).
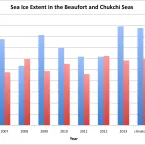
Nearly frozen up by the end of October, the Arctic Ocean still showed small regions of open water within the Beaufort and Chukchi seas on its western side, and within the Kara Sea on its eastern side.
This summer, Arctic sea ice loss was held in check by relatively cool and stormy conditions. As a result, 2013 saw substantially more ice at summer’s end, compared to last year’s record low extent.
On September 13, Arctic sea ice reached its likely minimum extent for 2013. The minimum ice extent was the sixth lowest* in the satellite record, and reinforces the long-term downward trend in Arctic ice extent.
Following a relatively cool summer, sea ice extent fell to a little over 5 million square kilometers (1.93 million square miles) over the first two weeks of September and is at or near the minimum extent for the year.
Sea ice continued its late-season summer decline through August at a near-average pace. Ice extent is still well above last year’s level, but below the 1981 to 2010 average.
Arctic sea ice extent maintained a steady, near-average pace of retreat through the first half of August, making it highly unlikely that a new record low minimum will be reached this year.
Following rapid ice loss in the first half of July, the pace of seasonal ice retreat slowed the rest of the month partly due to the return of a stormy weather pattern over the central Arctic Ocean.
Sea ice extent retreated fairly rapidly through the first two weeks of July as a high pressure cell moved into the central Arctic, bringing warmer temperatures over much of the Arctic Ocean.
Arctic sea ice continues to track below average but remains well above the levels seen last year. The relatively slow ice loss is a reflection of the prevailing temperature and wind patterns.
Arctic sea ice extent declined at a near-average rate through May, but overall it remained below average compared to the 1979 to 2000 average. The Arctic Oscillation (AO) varied through the month between modest positive and negative phases.
Arctic sea ice extent declined at an approximately average rate through April. While the Arctic Oscillation was in its negative phase for most of winter, in mid April it turned positive.