How to import NetCDF or HDF data into ArcGIS
This How to guide outlines the steps for properly importing, projecting and visualizing HDF and NetCDF files in ArcMap. A couple of things to note before you start:
It is only relevant to ESRI ArcMap 10.5 and later versions. If you are running ArcMap 10.4.1 there is a patch you can download. If you are working in older versions of ArcMap then please note there is a workaround for SMAP data sets, further details at the bottom of this article.
This guide uses a NetCDF file from the NOAA@NSIDC MASIE-NH dataset as an example, but these steps can be applied to HDF files as well, such as those from SMAP (e.g. SPL4SMGP). It also assumes that you have already downloaded the file that you wish to view in GIS.
Note for SMAP datasets: If you are using an older version of ArcMap and wish to import SMAP HDF files then the best course of action is to utilize NASA's Earthdata Search tool to order SMAP data in GeoTIFF format. If you are in need of guidance for the Earthdata tool, please read the Search, order and customize NSIDC DAAC data with NASA Earthdata Search article.
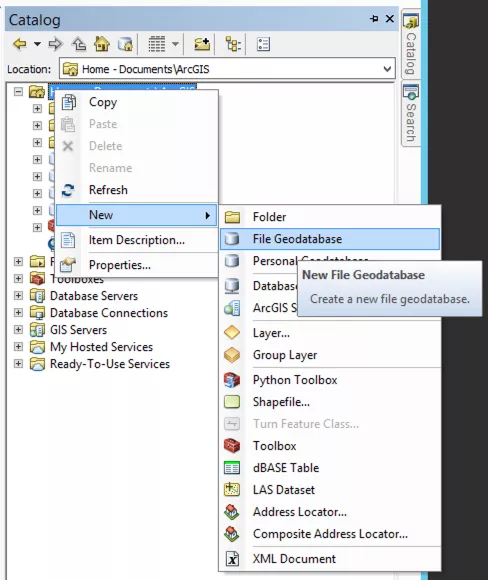
Step 1: Create a new file geodatabase
Open ArcMap with a blank map. Open the Catalog window and navigate to where you wish to create a new workspace. Right click on a folder connection and select 'New > File Geodatabase'. Then, name your new file geodatabase.
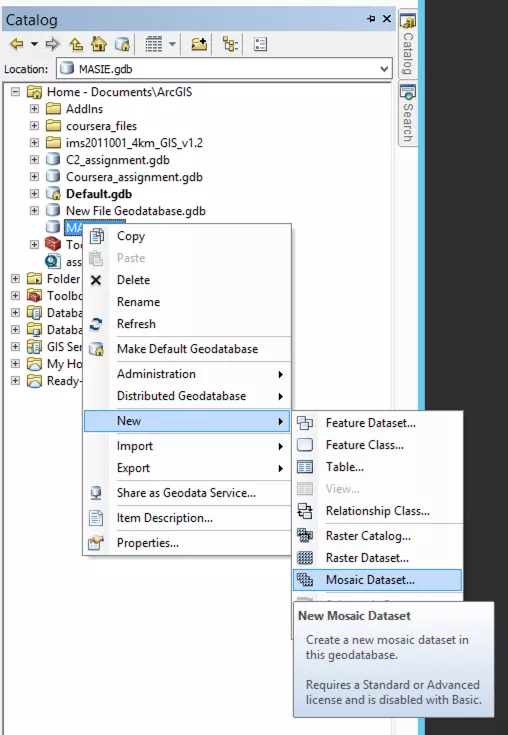
Step 2: Create a new mosaic dataset
Right click on the file geodatabase you just created and select 'New > Mosaic Dataset'.
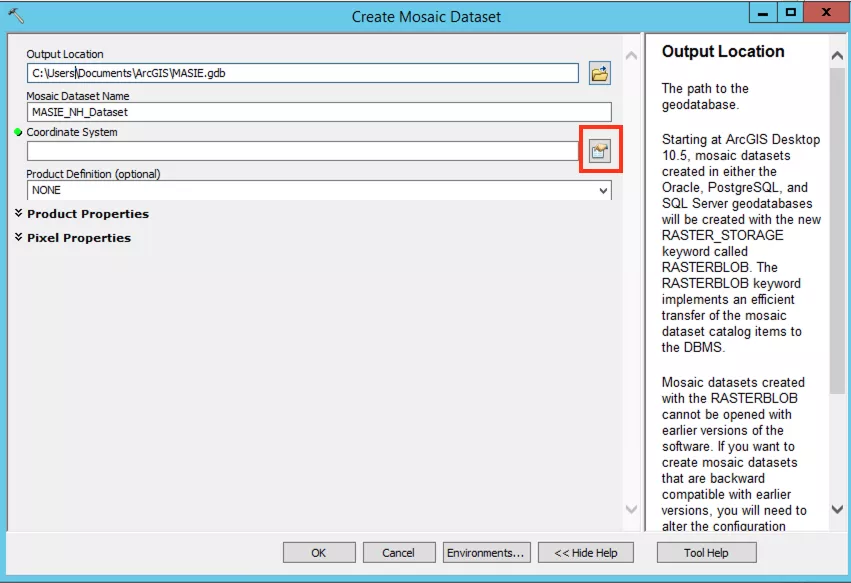
Step 2a: Name the mosaic dataset
In the new dialogue box add a name for the new mosaic dataset e.g. 'MASIE_NH_dataset'. Now you need to assign the correct projected coordinate system by clicking the card symbol to right of the Coordinate System box (highlighted by the red box in the image below). The projection you use will depend on the data set. Projection information can be found in the data set user guide.
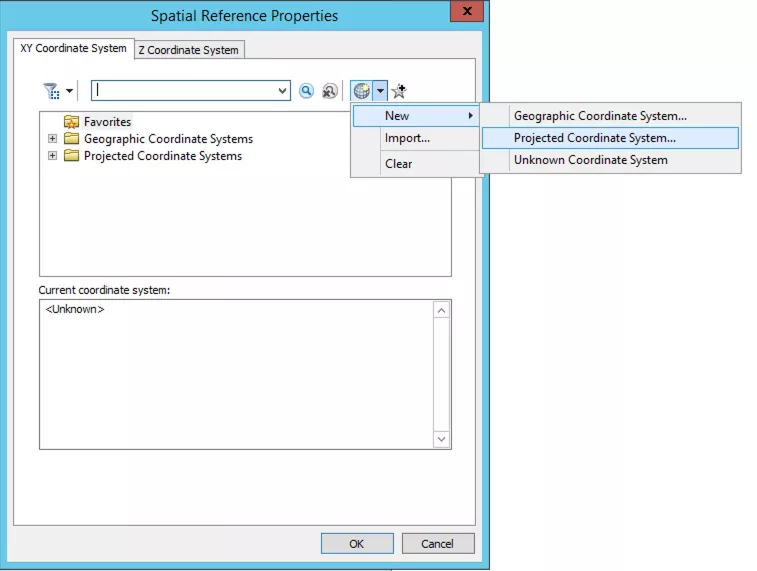
Step 2b: Assign projection for the mosaic dataset
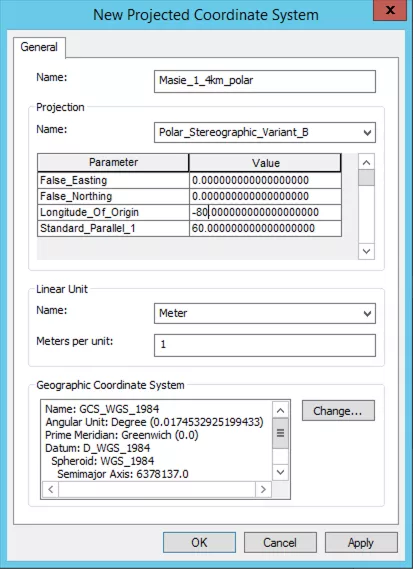
MASIE-NH uses a custom projection, which you will need to create. In the new dialogue box, select the globe button and 'New > Projected Coordinate System'.
In the dialogue box give your custom projection a name e.g. 'Masie_1_4km_polar'. Under the 'Projection Name' dropdown select 'Polar_Stereographic_Variant_B'. Set the 'Longitude_Of_Origin = -80'. Then, under 'Geographic Coordinate System' click the 'Change button.
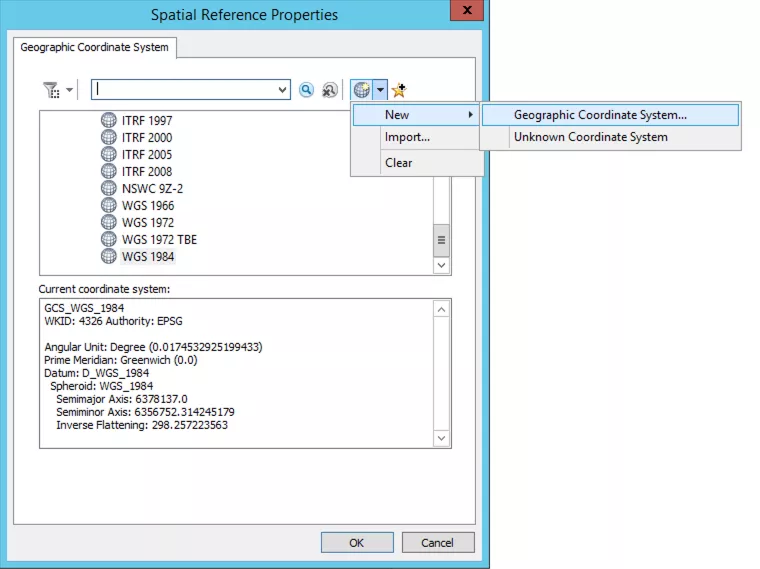
In the new dialogue box, click the globe button and select 'New > Geographic Coordinate System'.
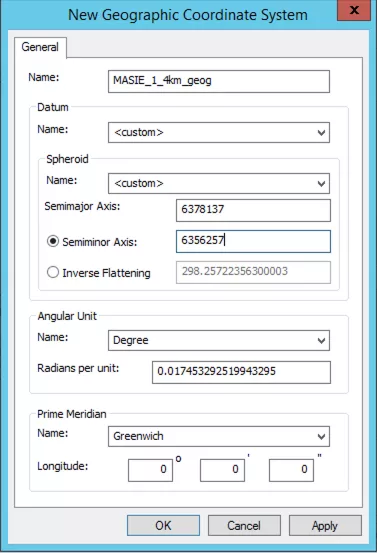
In the new dialogue box, give your custom geographic coordinate system a name e.g. 'masie_1_4km_geog'. Set the 'Datum' and 'Spheroid' to '<custom>'. Next, set the 'Semiminor Axis' to 6356257. Click 'OK' in each of the 4 dialog boxes to close them. You can skip the next step in this article and go to the section called Add the NetCDF or HDF file as a Raster)
Step 2c: Assign projection for mosaic dataset
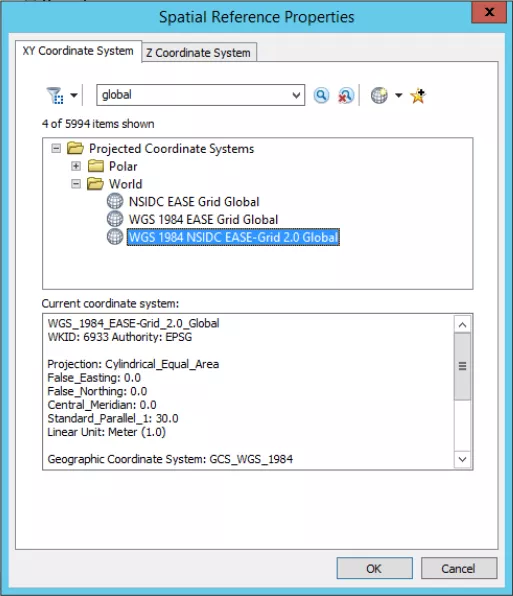
For other NetCDF or HDF files, you can search for the projection in the dialogue box. If you do not know the projection, this information can be found in the data set user guide. As an example, for SPL4SMGP the Coordinate System is "WGS_1984_NSIDC_EASE-2.0_Global", which is searchable in the dialogue box (see image below). Once you have assigned the correct coordinate system, click 'OK'.
Step 3: Add the NetCDF or HDF file as a raster
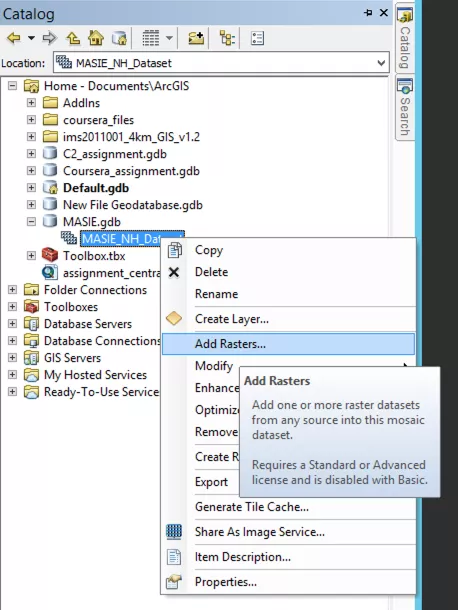
In the Catalog window, right click on the mosaic data set you have just created, and select 'Add Rasters...'.
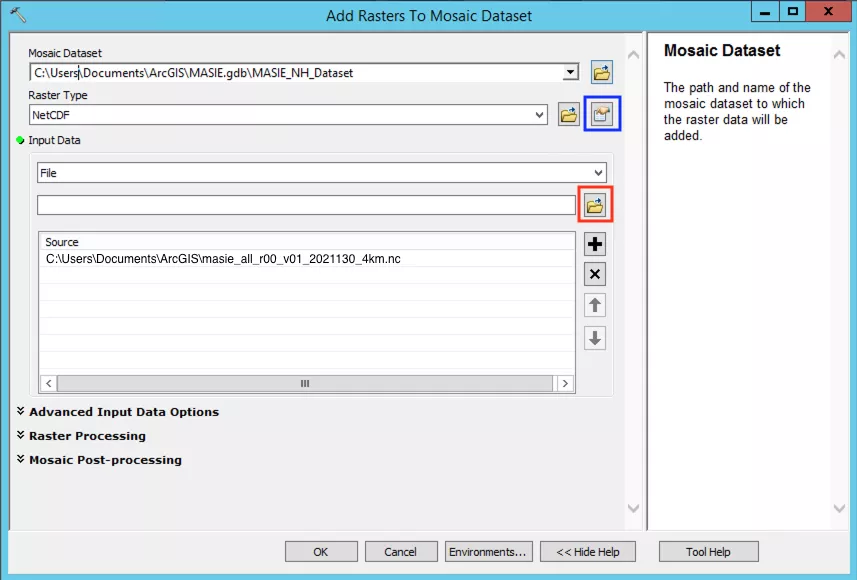
In the new dialogue box, from the 'Raster Type' dropdown select 'NetCDF' or 'HDF' depending on the file you are using. In the 'Input Data' dropdown select 'File'. Then, click the folder button below the dropdown (highlighted by a red box in the image below) and in the window that opens find the NetCDF or HDF file you wish to read in and click 'OK'.
Specify the NetCDF or HDF variable
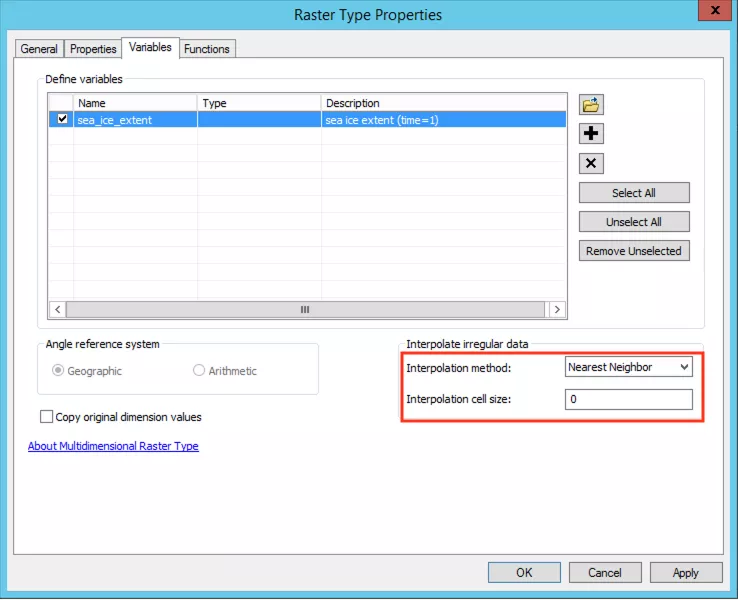
Next you need to specify the variable you wish to look at, and you can do so by clicking on the Properties box, to the right of the 'Raster Type' dropdown (highlighted by a blue box in the image above). In the new dialogue box, tick the box next to the variable you wish to look at and wait for the 'Interpolate Irregular Data' field to auto-fill (highlighted by the red box in the image below) and we recommend not changing these once they have auto-filled. Then click 'OK" twice to close both dialogue boxes and wait for the data to be loaded to the map, this can take several minutes.
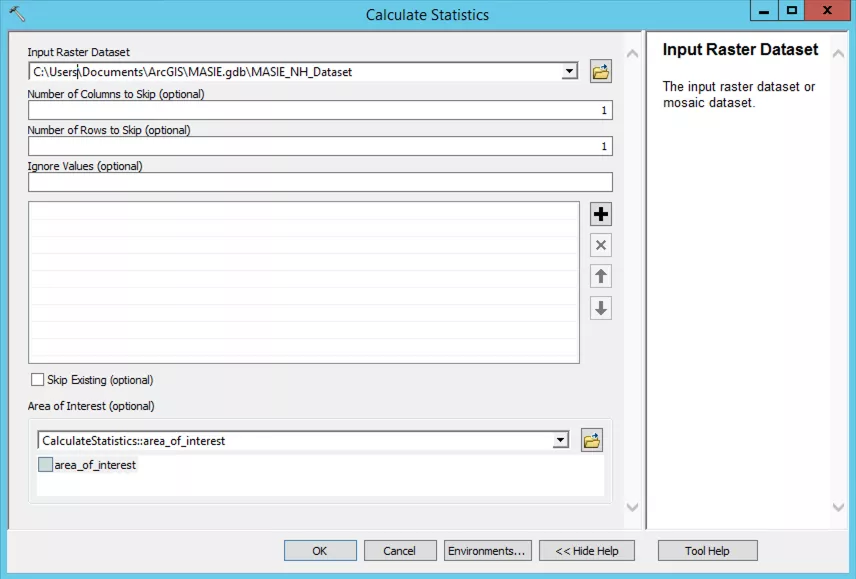
Calculate and specify min/max values
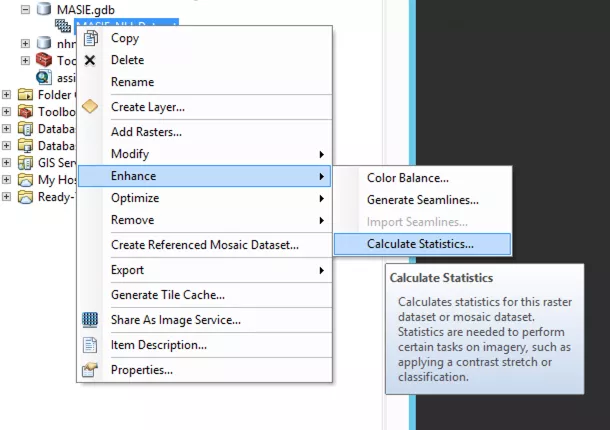
ArcMap does not know the min/max values, so we need to auto-fit the data for it to display properly. In the Catalog window, right click on the mosaic data set and select 'Enhance > Calculate Statistics'.
In the new dialogue box there are various options you can change but we recommend using the default settings, so go ahead and click 'OK'. This will calculate the min/max values and this can take several minutes.
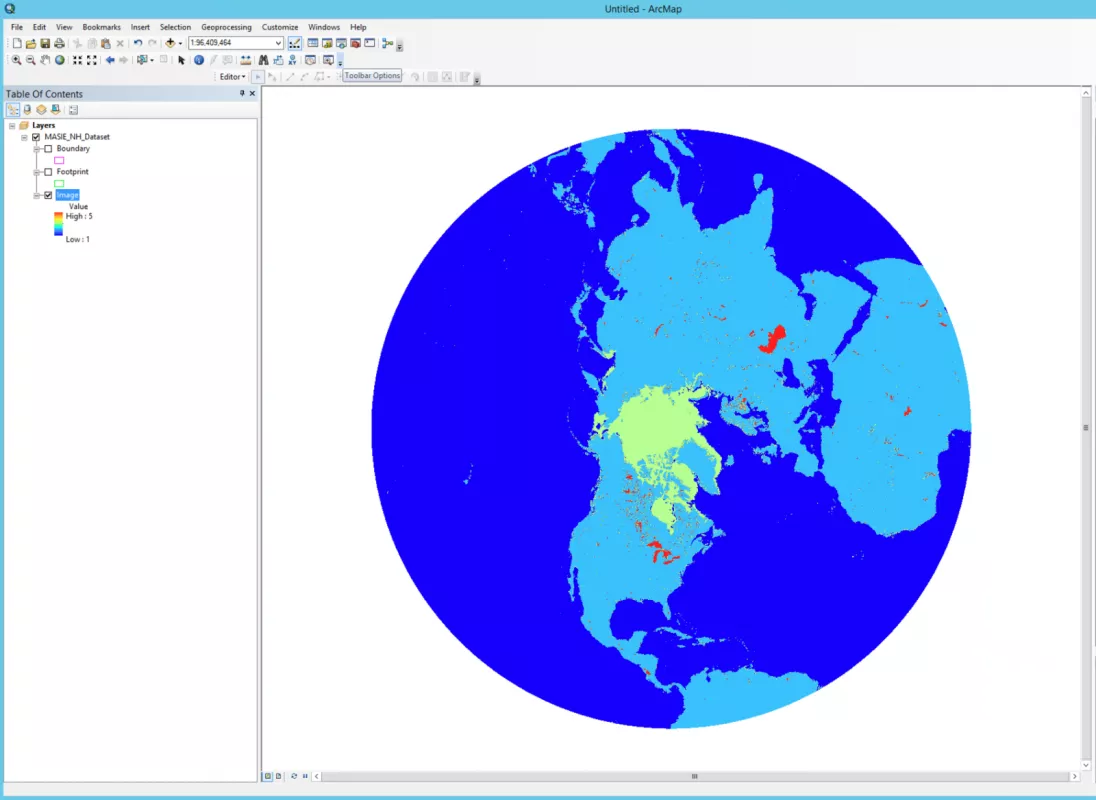
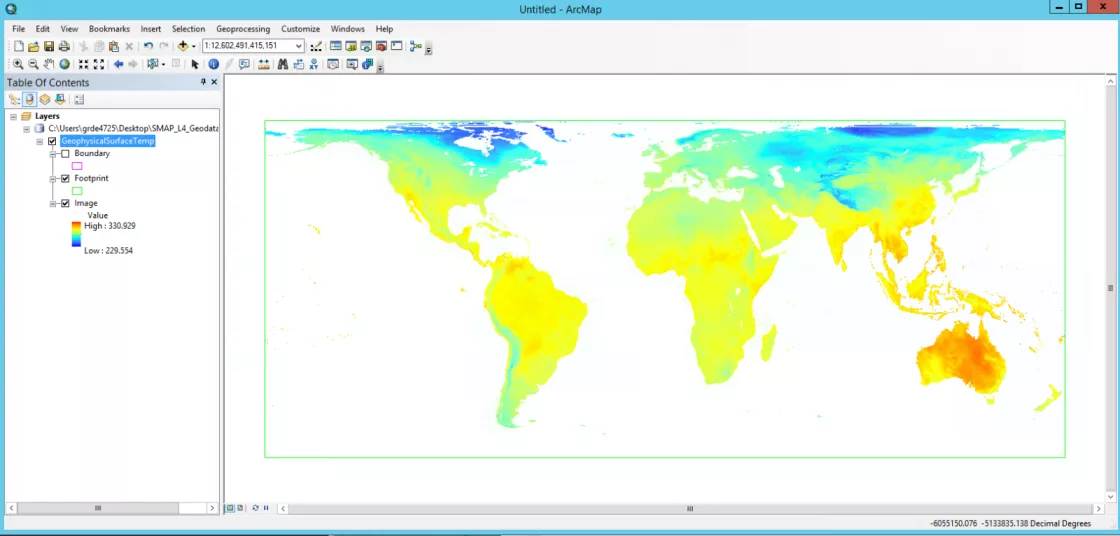
Step 4: Completed! Your HDF or NetCDF file has been imported
You have successfully imported your NetCDF or HDF into ArcMap. Below are examples of the output for a MASIE-NH NetCDF file and a SMAP SPL4SMGP HDF file.